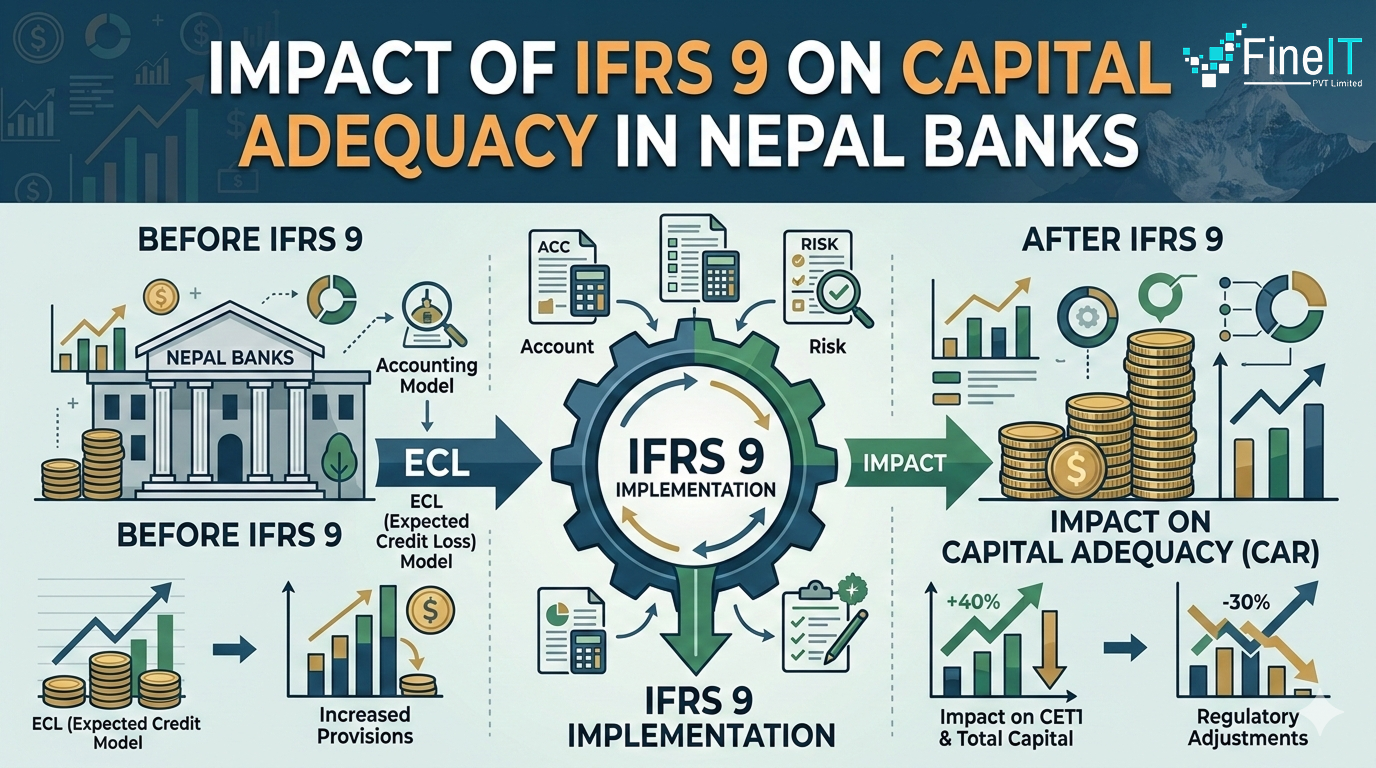
Data and Reporting Requirements for IFRS 9 in Nepal
Implementing the International Financial Reporting Standard 9 (IFRS 9)—localized as NFRS 9 in Nepal—marks a paradigm shift for the country’s financial landscape. As mandated by the Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB), this standard moves banks from a reactive “incurred loss” model to a proactive “Expected Credit Loss” (ECL) framework. The transition is data-intensive, requiring financial institutions […]